Pozioni
Le pozioni sono oggetti consumabili che conferiscono un effetto ad un'entità. Un giocatore può preparare delle pozioni usando l'Alambicco oppure ottenerle come oggetti attraverso varie meccaniche di gioco.
Pozioni Personalizzate
Aggiungere una pozione è simile al metodo per aggiungere un oggetto. Dovrai creare un'istanza della tua pozione e registrarla chiamando BrewingRecipeRegistry.registerPotionRecipe.
INFO
Quando Fabric API è presente, BrewingRecipeRegistry.registerPotionRecipe è reso disponibile attraverso un Access Widener.
Creare la Pozione
Inziamo dichiarando un attributo per conservare la tua istanza Pozione. Utilizzeremo direttamente la classe dell'initializer per conservarla.
java
public static final Potion TATER_POTION =
Registry.register(
Registries.POTION,
new Identifier("fabric-docs-reference", "tater"),
new Potion(
new StatusEffectInstance(
FabricDocsReferenceEffects.TATER_EFFECT,
3600,
0)));Passiamo una istanza di StatusEffectInstance, che prende 3 parametri:
StatusEffect type- Un effetto. Qui usiamo il nostro effetto custom. In alternativa puoi accedere agli effetti vanilla attraversonet.minecraft.entity.effect.StatusEffects.int duration- La durata dell'effetto espressa in game ticks.int amplifier- Un amplificatore per l'effetto. Ad sempio, Sollecitudine II (Haste II) avrebbe un amplificatore di 1.
INFO
Per creare il tuo effetto personalizzato, per favore guarda la guida Effetti.
Registrare la Pozione
Nel nostro initializer, chiamiamo BrewingRecipeRegistry.registerPotionRecipe.
java
BrewingRecipeRegistry.registerPotionRecipe(Potions.WATER, Items.POTATO, TATER_POTION);registerPotionRecipe prende 3 parametri:
Potion input- La pozione iniziale. Solitamente questo può essere una Ampolla d'Acqua (Water Bottle) o una Pozione Strana (Akward Potion).Item item- L'oggetto che rappresenta l'ingrediente principale della pozione.Potion output- La pozione risultante.
Se utilizzi Fabric API, il mixin invoker non è necessario, ed una chiamata diretta a BrewingRecipeRegistry.registerPotionRecipe può essere fatta.
L'esempio per intero:
java
public class FabricDocsReferencePotions implements ModInitializer {
public static final Potion TATER_POTION =
Registry.register(
Registries.POTION,
new Identifier("fabric-docs-reference", "tater"),
new Potion(
new StatusEffectInstance(
FabricDocsReferenceEffects.TATER_EFFECT,
3600,
0)));
@Override
public void onInitialize() {
BrewingRecipeRegistry.registerPotionRecipe(Potions.WATER, Items.POTATO, TATER_POTION);
// Use the mixin invoker if you are not using Fabric API
// BrewingRecipeRegistryInvoker.invokeRegisterPotionRecipe(Potions.WATER, Items.POTATO, TATER_POTION);
}
}Una volta registrato, puoi distillare una pozione di Tater usando una patata.
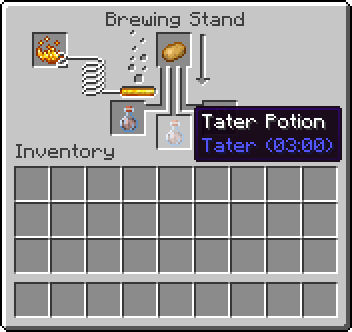
INFO
Registering Potions Using an Ingredient
Con l'aiuto di Fabric API, è possibile registrare una pozione usando un Ingrediente anziché un Item (oggetto) usando net.fabricmc.fabric.api.registry.FabricBrewingRecipeRegistry.
Registrare la Pozione senza Fabric API
Senza Fabric API, BrewingRecipeRegistry.registerPotionRecipe sarà privato. Per accedere a questo metodo usa il seguente mixin invoker o un Access Widener.
java
@Mixin(BrewingRecipeRegistry.class)
public interface BrewingRecipeRegistryInvoker {
@Invoker("registerPotionRecipe")
static void invokeRegisterPotionRecipe(Potion input, Item item, Potion output) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}

